Generate Electricity – How Solar Panels Work!

This lesson explores the functioning of solar panels, which convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. It explains the components of solar modules, the process of generating electric current, and the different types of solar cells, highlighting their efficiencies and applications. By understanding these concepts, we can appreciate the significance of solar energy as a clean and renewable power source.
Ductwork sizing, calculation and design for efficiency – HVAC Basics + full worked example
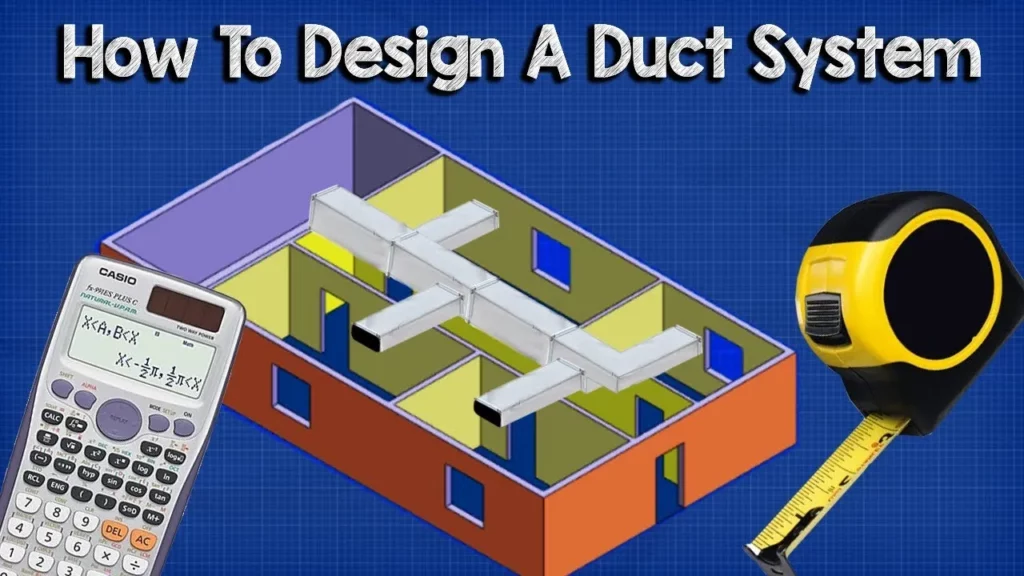
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of ductwork design for HVAC systems, focusing on the equal friction method for efficiency. It covers the process of calculating heating and cooling loads, converting these loads into volume flow rates, and sketching ductwork routes while considering dynamic losses and material impacts on efficiency. The lesson emphasizes the importance of optimizing duct design through simulations and careful planning to enhance airflow and reduce pressure losses.
DC parallel circuits explained – The basics how parallel circuits work working principle
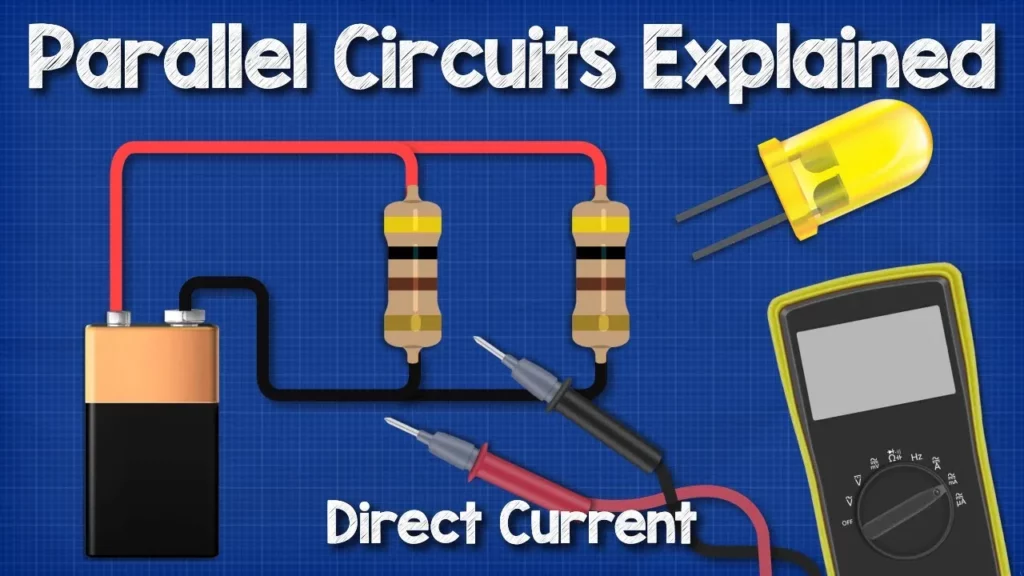
In this lesson, we explored the fundamentals of DC parallel circuits, focusing on their structure and how to calculate key electrical values such as voltage, current, and resistance. Unlike series circuits, where a single path can disrupt the flow of electricity, parallel circuits allow multiple paths for current, ensuring that if one component fails, others continue to operate. We also discussed relevant formulas, including Ohm’s Law and methods for calculating total resistance and power consumption, and concluded with practice problems to reinforce understanding.
Differential explained – How differential works open, limited slip
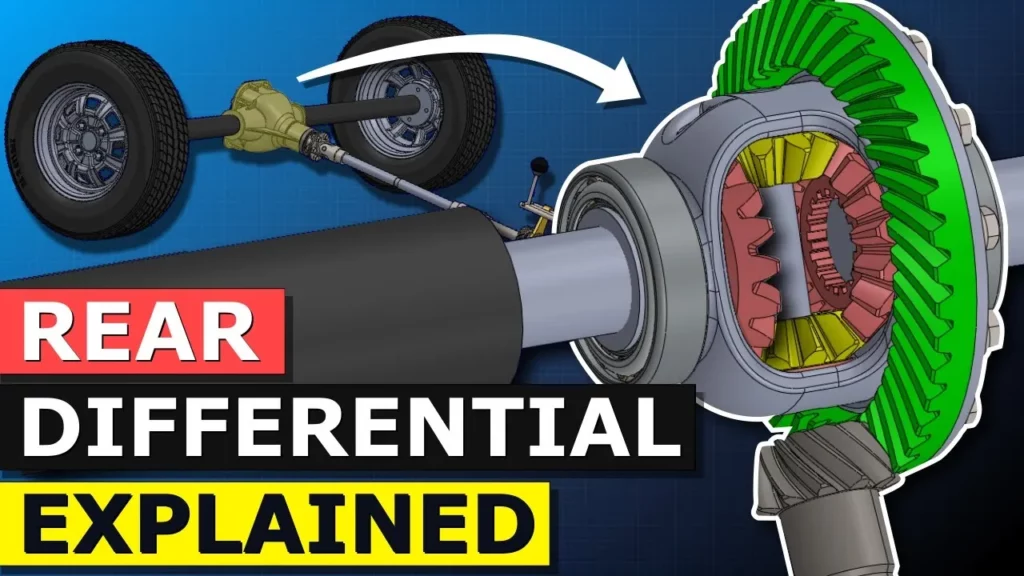
This lesson explains the function and importance of differential gear trains in vehicles, highlighting how they enable wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns to prevent tire slippage and improve handling. It contrasts open differentials, which can struggle on slippery surfaces, with limited slip differentials that enhance traction by distributing power more evenly. Additionally, the lesson encourages hands-on learning through model building to deepen understanding of these essential automotive components.
Why Electronics Need Cooling – transistor heat sink
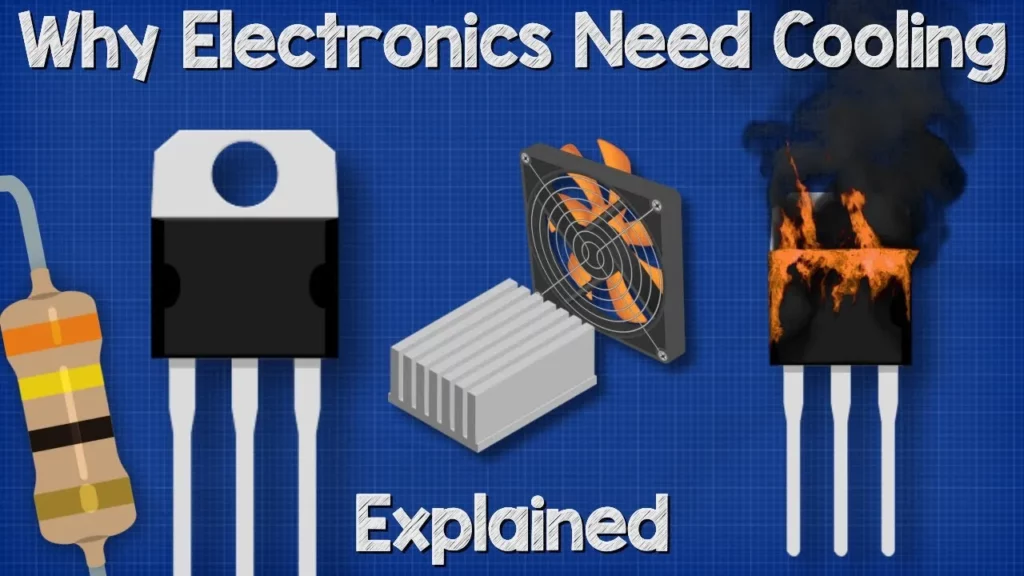
In this lesson, we explored the critical role of cooling in electronics, emphasizing the need to manage heat generated by components like resistors, MOSFETs, and IGBTs to prevent damage and ensure reliability. We discussed various cooling strategies, including heatsinks, fans, and advanced methods like liquid cooling, highlighting the importance of simulation tools for optimizing designs. Ultimately, effective cooling not only enhances performance and lifespan but also reduces operating costs in electronic systems.
How Potentiometer Works – Unravel the Mysteries of How potentiometers Work!

This lesson explains the function and application of potentiometers, which are adjustable resistors used to modify voltage and current in various electronic devices. It covers their construction, including the resistive track and wiper mechanism, as well as their ratings and types, such as linear and logarithmic. Potentiometers are commonly found in devices like game controllers and radios, serving as essential components for manual adjustments in circuits.
How to 3D Print Electric Motor

This lesson guides you through the process of building a 3D-printed electric motor using enameled copper wire and various materials. It covers the steps of creating the rotor, preparing copper plates, assembling the motor, and making electrical connections, ultimately allowing you to witness the motor in action. By following this tutorial, you’ll gain hands-on experience with electromagnetism and engineering principles.
Hybrid Stepper Motor Basics
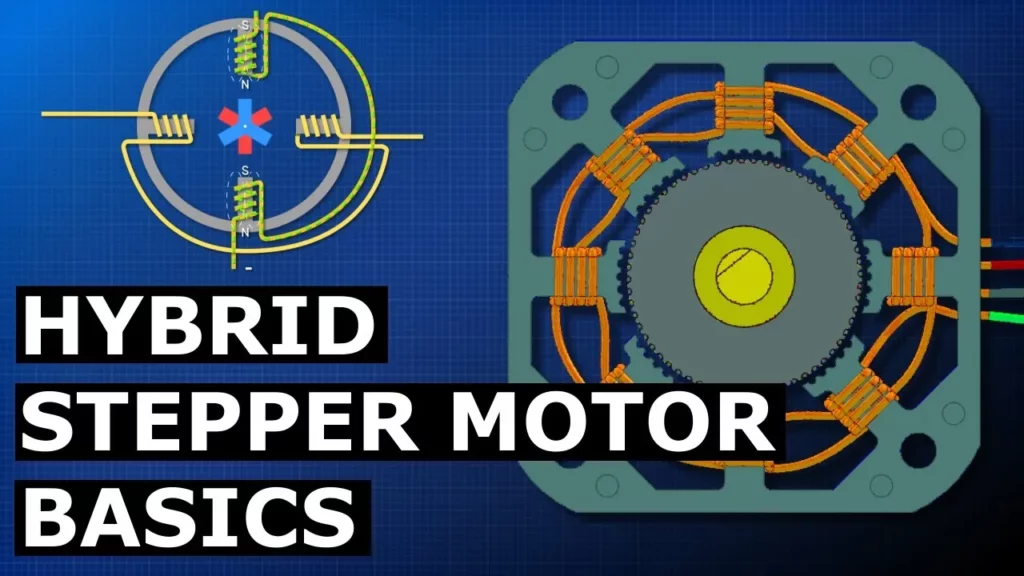
The lesson on hybrid stepper motors explains their operation and advantages, highlighting their combination of variable reluctance and permanent magnet technologies for precise movement control. It details how these motors function through the interaction of energized coils and the rotor’s magnetic fields, allowing for accurate positioning with each step, which can be as small as 1.8 degrees in advanced models. The lesson encourages further exploration of electrical engineering concepts and community engagement for deeper learning.
Capacitors in Parallel – calculations electronics engineering
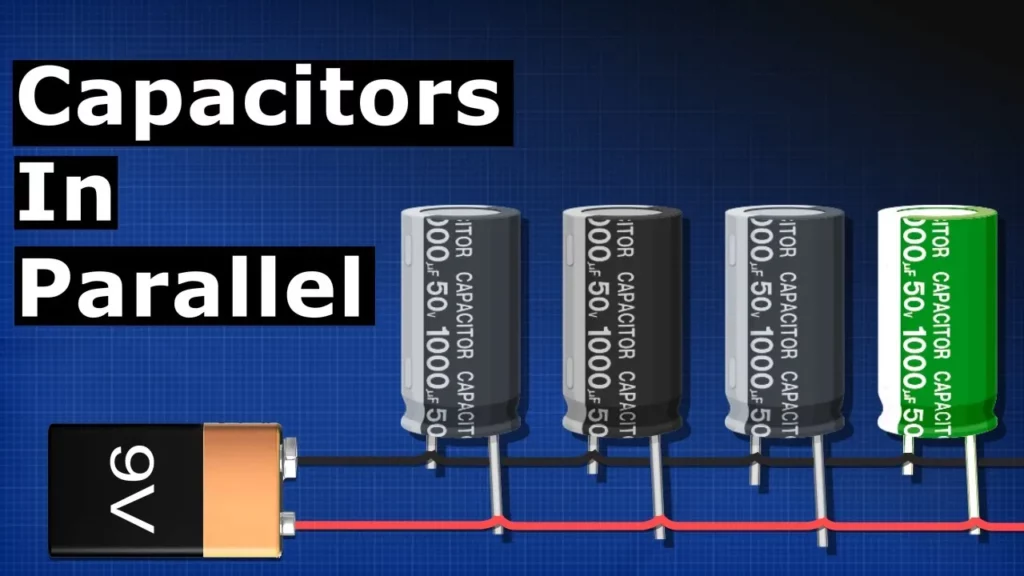
This lesson explains the concept of capacitors connected in parallel, highlighting their ability to store energy and extend the duration of power supply to devices like lamps. It covers how to calculate total capacitance by simply adding the capacitances of individual capacitors, and discusses practical applications, such as filtering electrical noise and providing additional current in high-demand circuits. Understanding these principles is vital for designing efficient electronic systems.
Electrical Current Explained – AC DC, fuses, circuit breakers, multimeter, GFCI, ampere
This lesson provides an overview of electrical current, explaining its nature as the flow of electrons through a circuit and the importance of voltage in initiating this flow. It distinguishes between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), discusses methods for measuring current using ammeters and multimeters, and highlights safety devices like fuses, circuit breakers, and GFCIs that protect against electrical overloads. Understanding these concepts is crucial for the safe and efficient use of electricity in everyday applications.