Constant Air Volume – CAV HVAC system basics hvacr

The lesson on Constant Air Volume (CAV) HVAC systems explains that CAV systems maintain a consistent volume of air while allowing temperature variations, making them suitable for buildings with similar cooling demands. Key components include the air handling unit, ductwork, and diffusers, but the system’s limitations include discomfort in spaces with varying needs and challenges in adapting to changing room functions. While newer Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems offer better energy efficiency and zone control, CAV systems can still be effective in specific applications, particularly in older buildings.
Power Inverters Explained – How do they work working principle IGBT
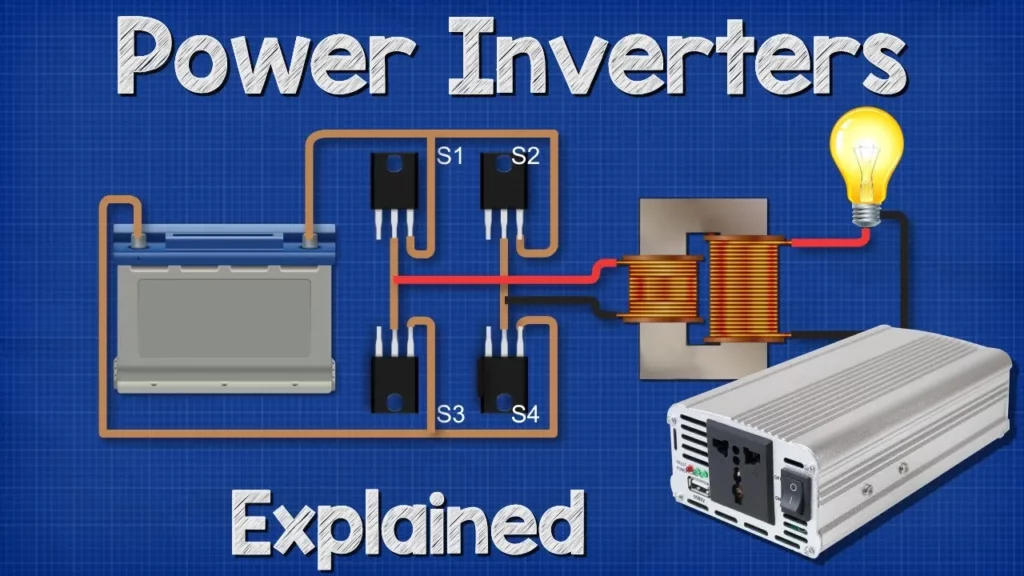
This lesson provides an overview of power inverters, which are devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to power household appliances. It explains the basic principles of electricity, how inverters function using electronic switches, and the importance of voltage transformation and waveform improvement to produce a clean AC output. Additionally, it touches on the differences between single-phase and three-phase electricity, highlighting their applications in residential and commercial settings.
Step Up Transformer Calculation Basics
This lesson covers the fundamentals of step-up transformers, which increase voltage while decreasing current, adhering to energy conservation principles. It explains how to calculate secondary voltage and current using the turns ratio formula, and emphasizes the importance of maintaining consistent power on both sides of the transformer. Additionally, it encourages further exploration of electrical engineering concepts through various resources.
Why do we connect batteries?
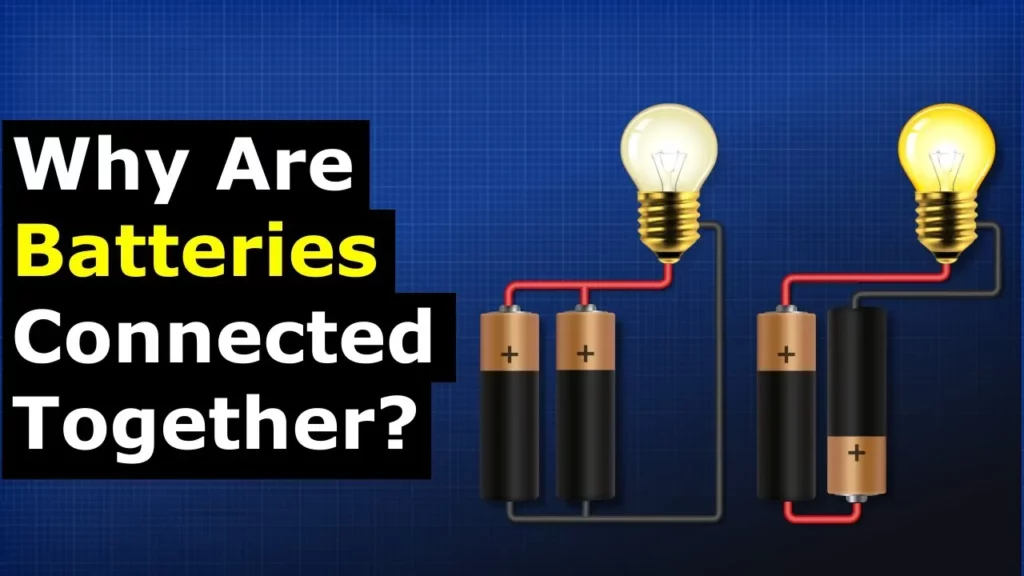
In this lesson, we learned about the two primary methods of connecting batteries: in series and in parallel. Connecting batteries in series increases the total voltage while keeping the capacity the same, whereas connecting them in parallel maintains the voltage but enhances the overall capacity, allowing for longer usage. Additionally, we explored how to measure battery voltage and test batteries under load to assess their performance.
Solenoid Basics Explained – Working Principle
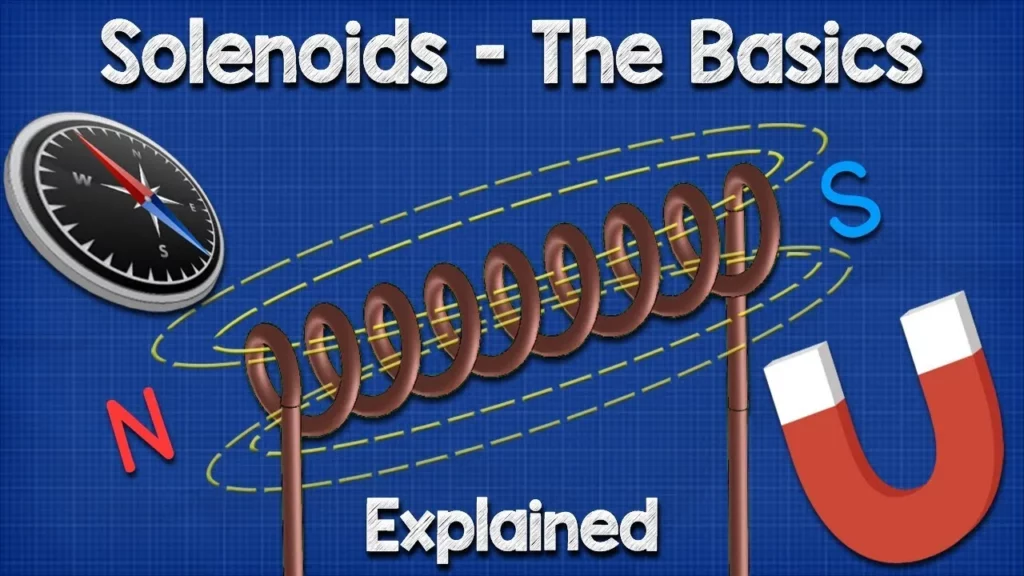
In this lesson, we explored the fundamentals of solenoids, focusing on the differences between permanent magnets and electromagnets. We learned how to create an electromagnet by coiling wire and connecting it to a power source, and we built a simple solenoid using a pen and enameled wire, demonstrating how an electromagnetic field can move an iron nail. The lesson also highlighted the practical applications of solenoids, such as in solenoid valves, and encouraged further exploration of related engineering concepts.
Basic Refrigeration cycle – How it works
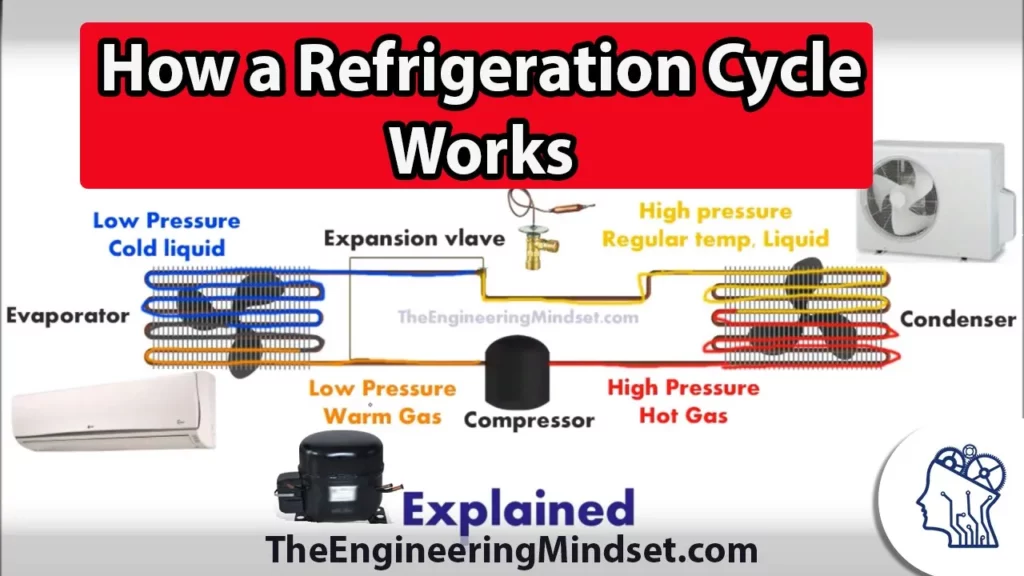
This lesson provides an overview of the refrigeration cycle, a crucial process in cooling systems like air conditioners and refrigerators. It explains the role of the refrigerant as it circulates through four key components—compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator—each contributing to the transfer of heat and the cooling of indoor spaces. By understanding these fundamentals, learners can build a foundation for further exploration of refrigeration technology.
3 Phase Inverter Basics – Working Principle

This lesson covers the fundamentals of three-phase inverters, which are essential for applications like powering large cooling system compressors. It explains the conversion process from a rectified three-phase AC source to a smooth DC supply, followed by the transformation of that DC into three-phase AC using six Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs). The lesson emphasizes the importance of synchronized switching sequences and introduces pulse width modulation (PWM) for generating a more precise sine wave output, highlighting the significance of mastering these concepts for efficient power conversion.
Thermostatic Radiator Traps – Steam heating HVAC

Thermostatic radiator traps are crucial for the efficiency of two-pipe steam heating systems, commonly used in older buildings. They function by allowing air and condensate to exit while preventing steam from escaping into the return line, thus ensuring effective heat distribution. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the traps are essential to avoid energy loss and maintain consistent heating performance.
How Wind Turbines Really Work: The Hidden Secrets

The lesson explores the intricate workings of wind turbines, detailing how they convert wind energy into electricity through mechanical processes. It highlights the importance of turbine design, including the optimal number of blades and their height, to maximize efficiency and energy capture. Additionally, the lesson discusses the components and technologies involved, such as generators and gearboxes, that ensure consistent power output and compatibility with electrical grids.
How Electric Motors Work – 3 phase AC induction motors ac motor
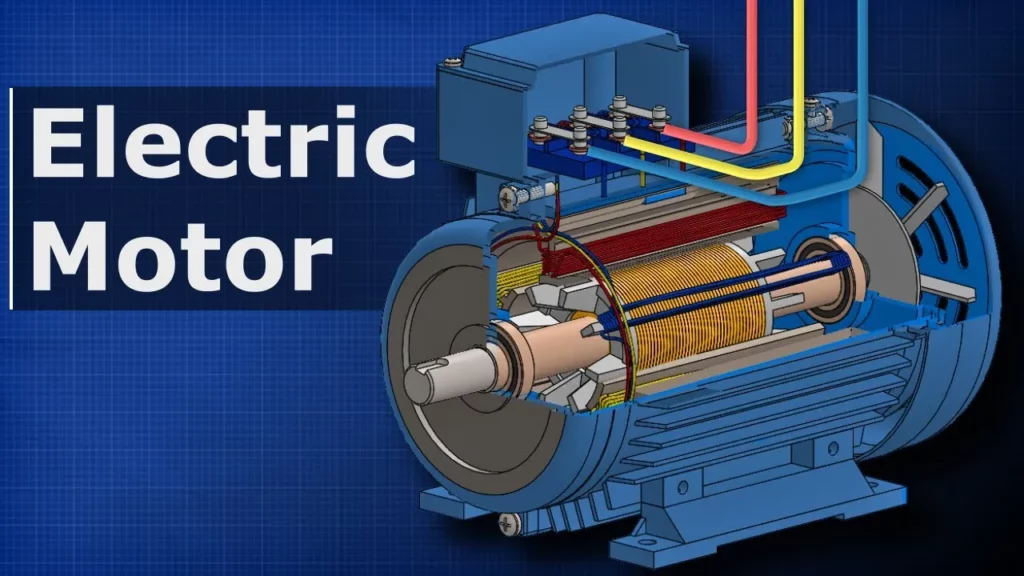
This lesson explains the functioning of three-phase AC induction motors, which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to power various machines. Key components include the stator, which generates a rotating electromagnetic field, and the rotor, which interacts with this field to create motion. The lesson also covers motor configurations, specifically Delta and Star, highlighting their differences in voltage exposure and current flow.