How TXV works – Thermostatic expansion valve working principle, HVAC Basics vrv heat pump
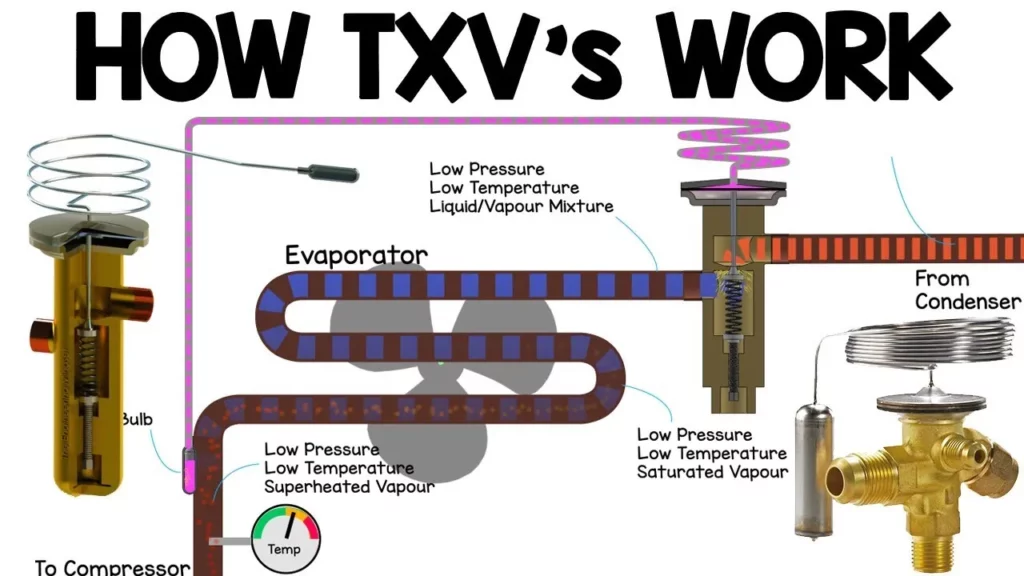
The lesson on the Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) in HVAC systems highlights its essential role in regulating refrigerant flow within refrigeration systems, including its key components such as the valve body, diaphragm, and sensing bulb. The TXV operates by reducing the pressure of the refrigerant before it enters the evaporator, allowing for efficient heat absorption and maintaining optimal superheat levels. Understanding the TXV’s functionality and potential failure implications is crucial for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of refrigeration systems.
Power Factor Explained – The basics what is power factor pf
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of power factor, a key concept in electrical engineering that measures the efficiency of power usage in AC circuits. It explains the relationship between true power, reactive power, and apparent power, using relatable analogies and examples to illustrate how power factor affects energy consumption and costs, particularly in commercial and industrial settings. The lesson also discusses the causes of poor power factor and methods for correction, emphasizing the importance of maintaining an optimal power factor to avoid penalties and enhance equipment performance.
Single Phase Electricity Explained – wiring diagram energy meter
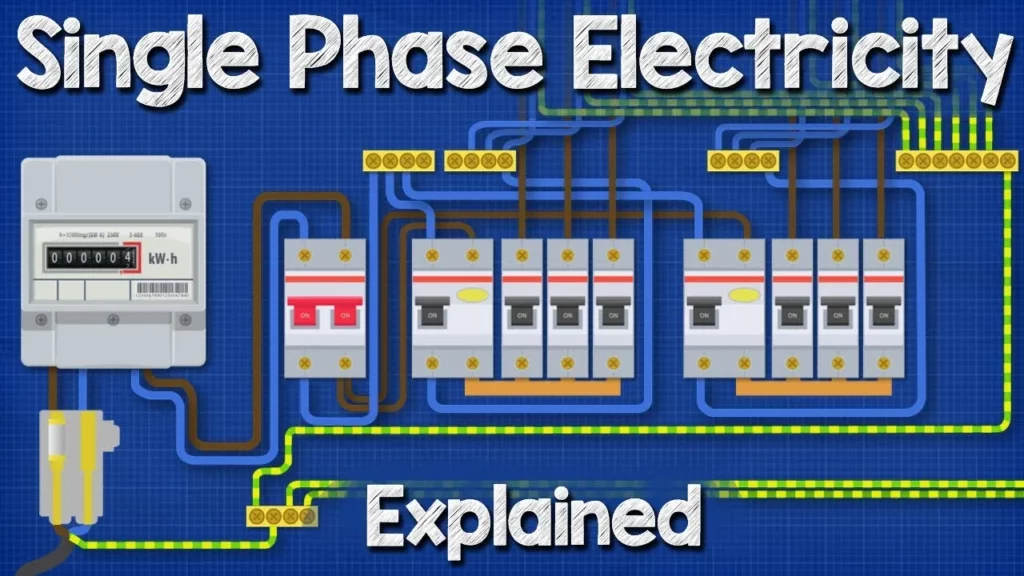
This lesson provides an overview of single-phase electricity supply, commonly used in residential areas across various regions, including the UK and Europe. It explains the journey of electricity from generation at power stations to its distribution through transformers and service cables into homes, highlighting key components such as the main fuse, electricity meter, consumer unit, and safety devices like RCDs and MCBs. The lesson emphasizes the importance of safety measures, including earth cables, to protect against electrical hazards.
Design and Build a PCB – SMD LED Learn electronics engineering

This lesson provides a comprehensive guide on designing and building a printed circuit board (PCB) using surface mount device (SMD) LEDs, emphasizing the importance of understanding component specifications and circuit design principles. It covers the selection of power supplies, the arrangement of LEDs in parallel, resistor calculations for current regulation, and the PCB layout process, culminating in the assembly and testing of the completed circuit. By following this guide, learners gain practical experience in electronics engineering and are encouraged to further explore the field.
How Transistors Work

The lesson explains the functioning of transistors using a water flow analogy, illustrating how an NPN transistor controls current flow through the manipulation of electron movement. It covers the roles of conductors, insulators, and semiconductors, detailing how doping silicon creates p-n junctions that enable transistors to switch and amplify electrical signals. By understanding the structure and operation of transistors, learners gain insight into their essential role in electronics.
How EEV works – Electronic Expansion Valve working principle, HVAC Basics
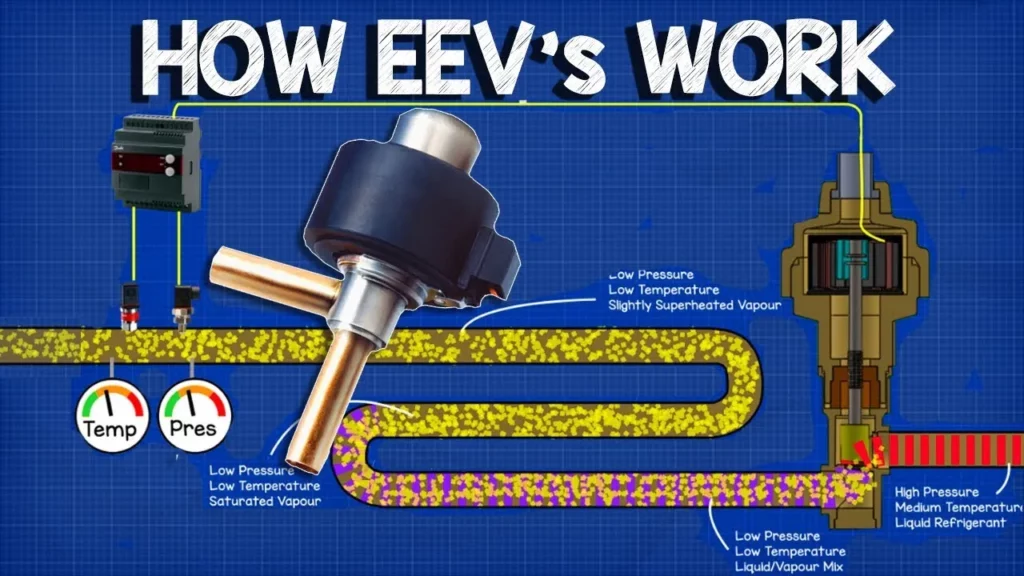
This lesson provides an overview of electronic expansion valves (EEVs) and their crucial role in HVAC systems, highlighting their advantages over traditional thermal expansion valves. EEVs enhance efficiency and precision in controlling refrigerant flow, which is essential for optimizing system performance in various applications such as chillers and heat pumps. The lesson also explains the components and functioning of EEVs, emphasizing their importance in modern refrigeration technology.
How a Chiller, Cooling Tower and Air Handling Unit work together
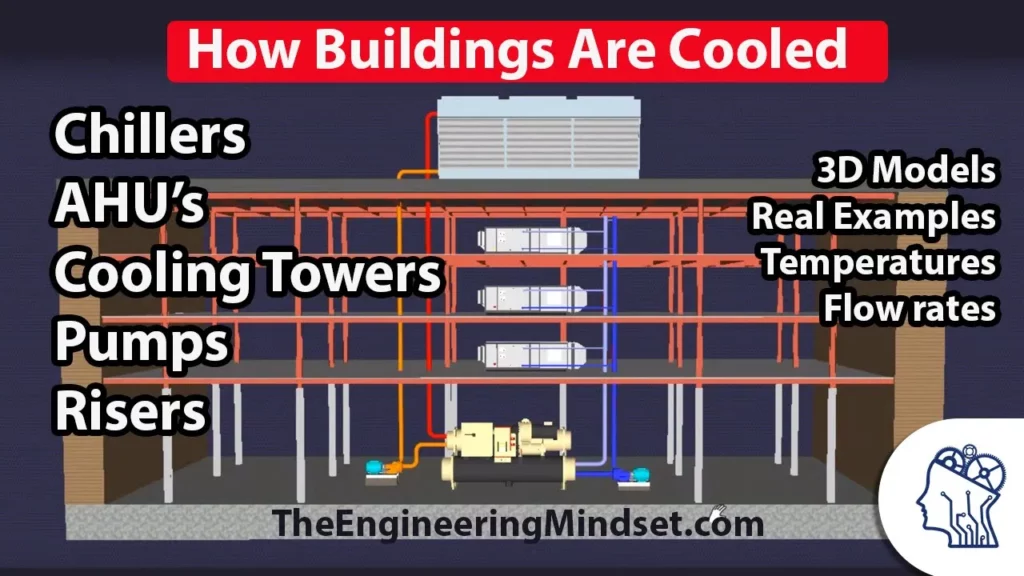
This lesson provides an overview of how a centralized chilled water system operates, highlighting the interaction between key components: the chiller, cooling tower, and air handling units. The chiller generates chilled water, which is circulated through the building to cool indoor air, while the cooling tower dissipates heat from the water before it returns to the chiller. The lesson emphasizes the importance of these components working together to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, especially in larger buildings with more complex systems for redundancy and efficiency.
Centrifugal Pump Basics – How centrifugal pumps work working principle hvacr
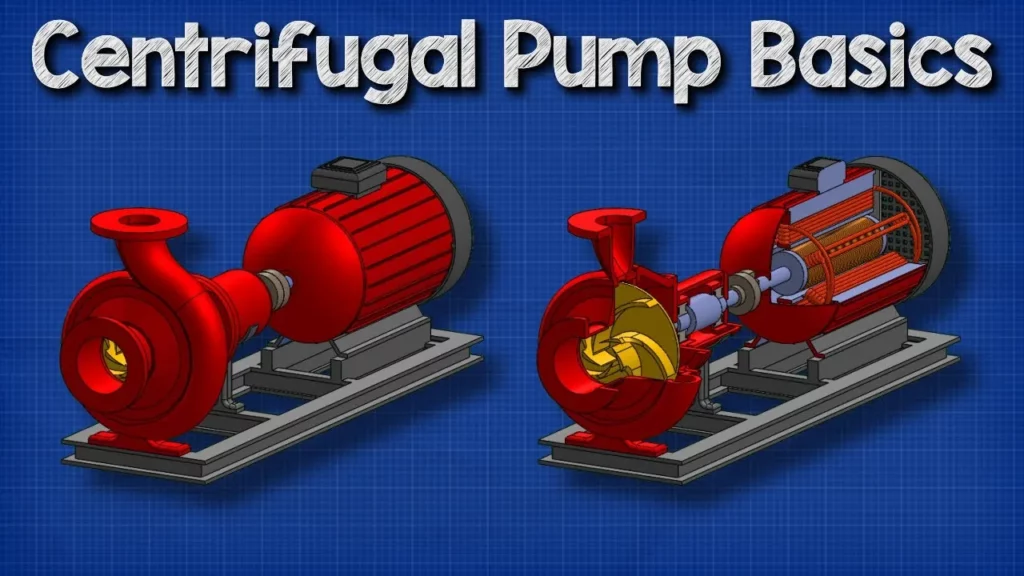
This lesson provides an overview of centrifugal pumps, detailing their components, operation, and applications. It explains how these pumps utilize an electric motor to create centrifugal force, which moves fluids efficiently through a system while emphasizing the importance of concepts like Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) to prevent cavitation. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for anyone studying engineering or interested in mechanical systems.
How Thermocouples Work – basic working principle + RTD
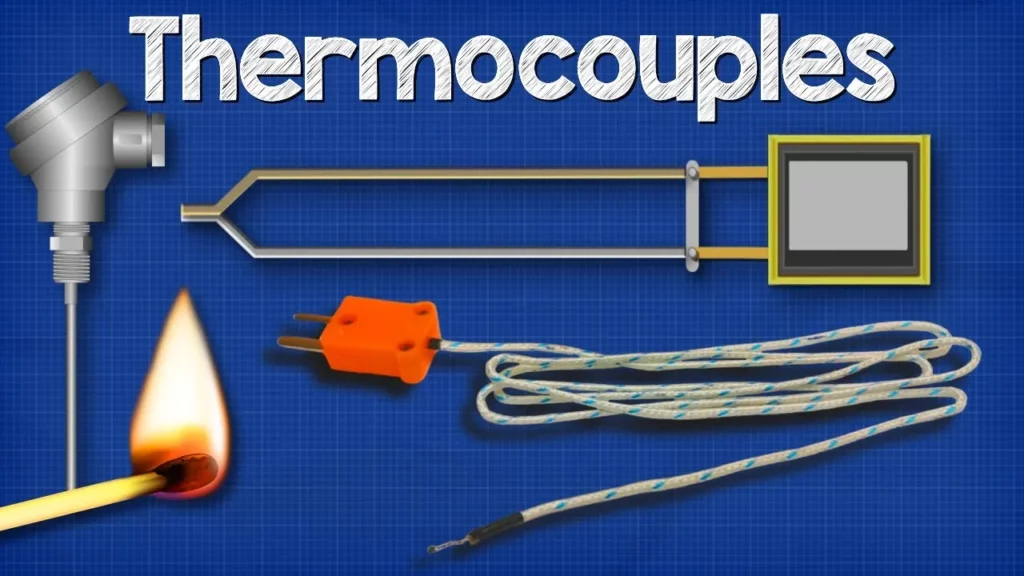
This lesson provides an overview of thermocouples and Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), two essential devices for temperature measurement. Thermocouples operate on the Seebeck effect, generating a voltage from the junction of two different metals exposed to heat, while RTDs measure temperature by detecting changes in the resistance of materials, typically platinum. Both devices are crucial in various applications due to their accuracy, reliability, and ability to function in diverse environments.
How A Car Battery Works – basic working principle
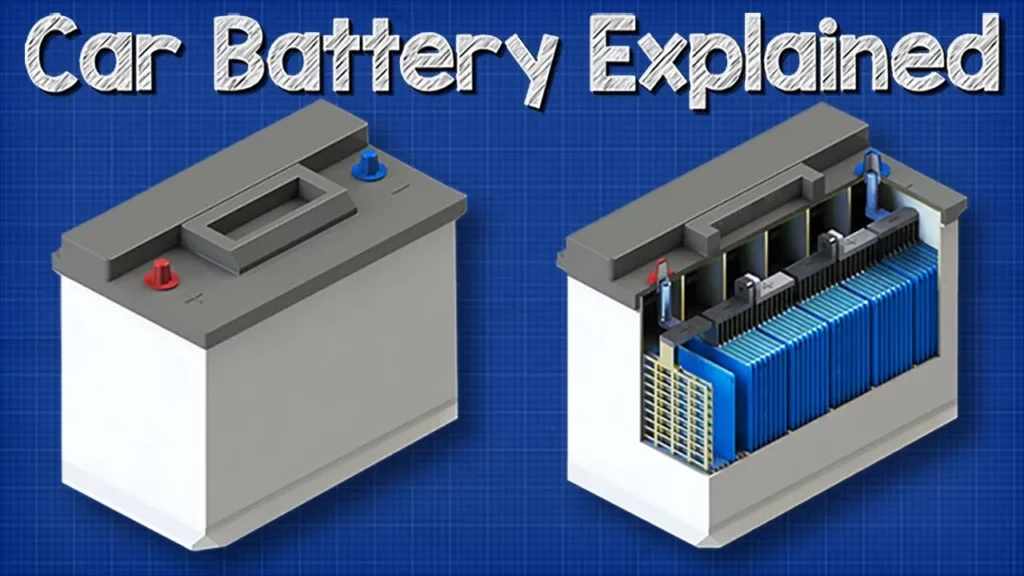
The lesson explains the basic working principle of a 12-volt lead-acid car battery, highlighting its role in starting and powering a vehicle. It details the battery’s structure, the chemical reactions that occur within it, and how it stores and converts energy. Additionally, the lesson covers the recharging process facilitated by the alternator and provides insights on checking battery health.