Inductors Explained – The basics how inductors work working principle
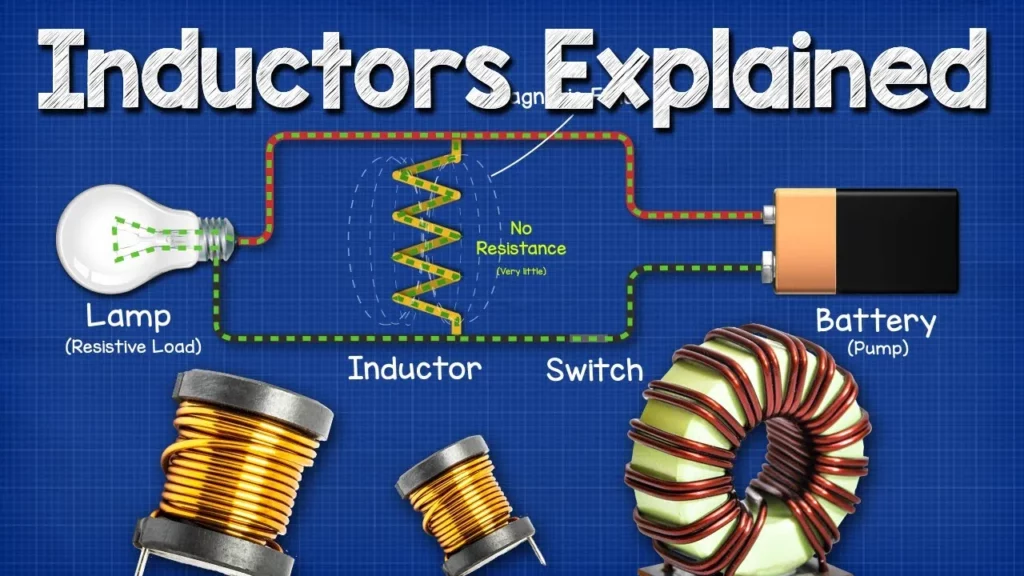
This lesson provides an in-depth understanding of inductors, highlighting their function as energy storage devices in electrical circuits through the creation of magnetic fields. It explains how inductors resist changes in current, their applications in various electronic systems, and the importance of safety when working with electrical components. Additionally, the lesson uses analogies and practical examples to illustrate the behavior of inductors in circuits, emphasizing their critical role in energy management and stability.
Ground Neutral and Hot wires explained – electrical engineering grounding ground fault
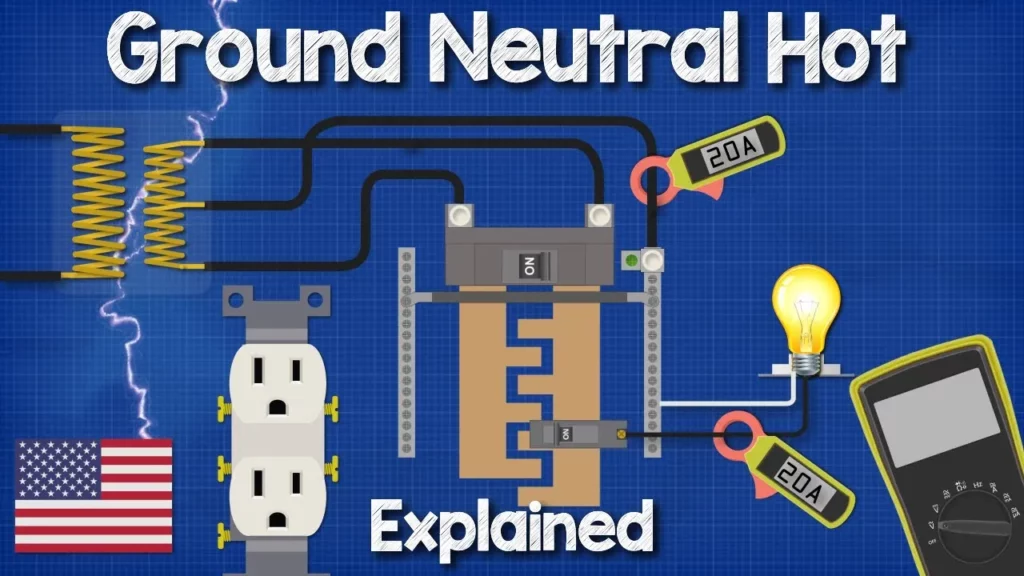
This lesson provides an overview of the roles and functions of hot, neutral, and ground wires in residential electrical systems, particularly in North America. It explains how electricity flows in a complete circuit, the differences between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), and the importance of grounding for safety. Additionally, it highlights the function of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) and ground rods in protecting against electrical faults and lightning strikes, emphasizing the need for safety and professional guidance in electrical work.
Induction Motor Basics

Induction motors are essential devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, powering various machines such as pumps and fans. They consist of key components like the stator, which generates a rotating electromagnetic field, and the rotor, which rotates in response to this field. The design and operation of induction motors, particularly the three-phase system, ensure continuous rotation and efficiency, making them vital in modern engineering applications.
3 Way Switches Explained – How to wire 3 way light switch
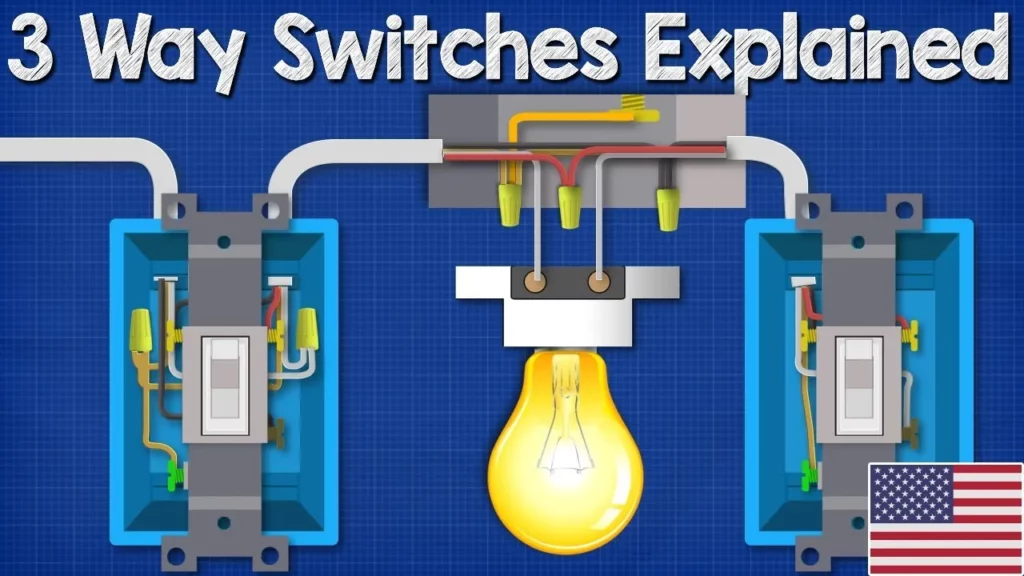
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of three-way switches used in lighting circuits, detailing three circuit designs based on the light fitting’s placement: at the beginning, middle, or end of the circuit. It emphasizes the importance of safety when working with electricity and offers step-by-step wiring instructions for each configuration, ensuring proper connections and grounding to control lighting effectively. For those seeking further information, additional resources are available for enhanced learning.
Constant Air Volume – CAV HVAC System
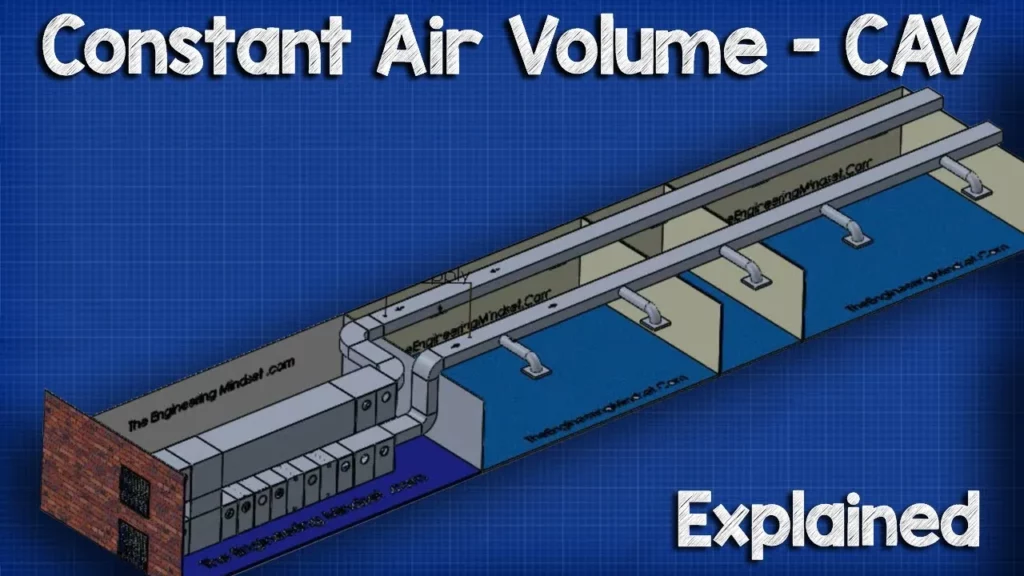
The lesson on Constant Air Volume (CAV) HVAC systems highlights their traditional role in providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, particularly in smaller or older buildings. While CAV systems maintain a constant volume of air, they face challenges in energy efficiency and zone control, as all connected spaces receive the same air temperature regardless of individual needs. Understanding the operation and limitations of CAV systems is essential for making informed HVAC decisions, especially as newer Variable Air Volume (VAV) systems become more prevalent.
How Inductors Work

The lesson explains the functioning of inductors in electrical circuits by using a water flow analogy. It illustrates how inductors resist changes in current, initially opposing the flow but eventually allowing it as they build a magnetic field. When power is cut, inductors release stored energy to maintain current flow briefly, demonstrating their crucial role in managing current in circuits.
Main electrical panel explained – Load center – service panel
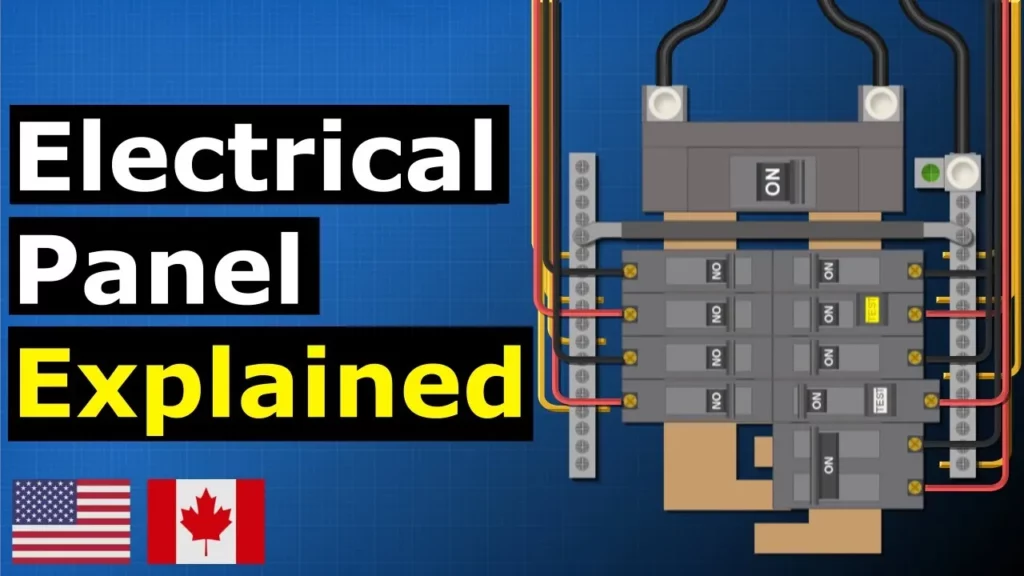
The lesson on the main electrical panel, also known as the load center or service panel, emphasizes the importance of understanding electrical systems for safety and efficiency. It covers the role of the main breaker in managing power distribution and providing overcurrent protection, as well as the functions of circuit breakers, grounding, and bonding to ensure safe electricity flow throughout a residential property. Additionally, specialized breakers like GFCI and AFCI are highlighted for their protective roles in preventing electrical hazards.
Ohms Law Explained – The basics circuit theory

In this lesson on Ohm’s Law, we explored the fundamental relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits, as established by physicist Georg Ohm. The key formulas—Voltage = Current × Resistance, Current = Voltage ÷ Resistance, and Resistance = Voltage ÷ Current—were introduced, along with practical examples to illustrate their application. Additionally, we discussed the reasoning behind the use of ‘I’ for current and provided practice problems to reinforce understanding.
Heat Pumps Explained – How Heat Pumps Work HVAC
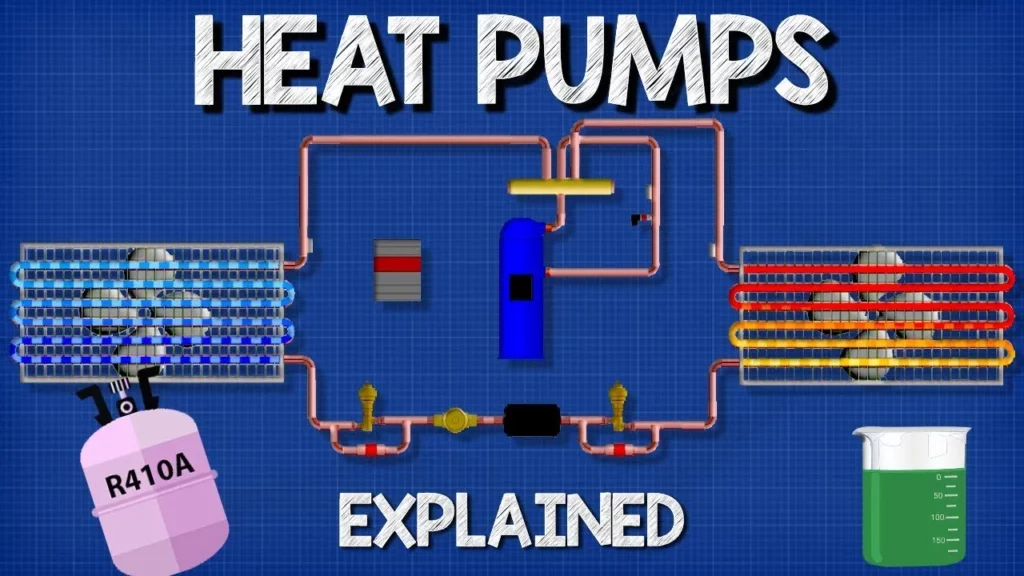
In this lesson, we explored the various types of heat pumps, including air-to-air, air-to-water, ground source, and water source systems, and examined how they function to provide efficient heating and cooling solutions. Heat pumps operate by transferring heat rather than generating it, making them an energy-efficient choice for both residential and commercial applications. Understanding the mechanics and benefits of each type can help individuals make informed decisions about their heating and cooling needs.
Why Cars Have a Starter Motor

The lesson explains the essential function of the starter motor in vehicles with combustion engines, highlighting its role in converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to initiate the engine’s combustion process. It details how the starter motor engages with the flywheel to rotate the crankshaft and move the pistons, allowing the engine to start efficiently and safely, in contrast to the manual methods used in early automobiles. Additionally, the lesson touches on the interaction between the starter motor, battery, and alternator, emphasizing the importance of understanding these components for automotive knowledge.