How does an Electric Motor work? (DC Motor)

This lesson provides an overview of how a DC motor operates, detailing its structure and key components, including the stator, rotor, magnets, and commutator. It explains the process of converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through the generation of electromagnetic fields and the role of brushes and commutators in facilitating current flow. Understanding these elements is essential for grasping the principles of motor technology and engineering.
AC Basics: Learn All About Alternating Current

The lesson on Alternating Current (AC) explains the fundamental principles of AC electricity, including its generation through rotating magnets and coils, which creates a sine wave pattern. It highlights the differences between single-phase and three-phase electricity, emphasizing the efficiency of three-phase systems in power distribution. Understanding AC is essential for recognizing its significance in powering homes and industries.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger basics explained

This lesson covers the fundamentals of shell and tube heat exchangers, which are essential for efficient heat transfer between two fluids in various industrial applications. It explains the components and functionality of these devices, including the role of headers, tubes, and baffles in optimizing heat exchange, as well as their applications in industries like pharmaceuticals and refrigeration. Additionally, the lesson briefly discusses alternative heat exchanger designs, such as double pipe and hairpin heat exchangers, highlighting their unique features and efficiencies.
Pump head pressure basics

The lesson on “Pump Head Pressure Basics” explains the concept of head pressure in pumps, which measures the height a pump can lift a liquid, rather than the specific pressure, due to varying liquid properties. Understanding head pressure is essential for selecting the right pump, as it helps account for frictional losses in piping systems, ensuring efficient liquid transport. Additionally, the lesson covers how to interpret pump charts, which display the relationship between head pressure and flow rate, and emphasizes the importance of maintaining optimal pump operation to prevent damage.
What is a Stepper Motor?

This lesson provides an overview of stepper motors, highlighting their unique ability to convert electrical energy into precise mechanical movements through controlled sequences of DC electricity. Unlike standard DC motors, stepper motors can rotate in small, accurate steps, making them essential in applications such as 3D printing and CNC machining. The lesson also explains the role of motor drivers and controllers in managing the motor’s operation, emphasizing the importance of precise electrical pulses for achieving desired movement.
Circulating pump: What is it & why is it important?

Circulating pumps are vital components in heating systems, primarily functioning as inline centrifugal pumps that efficiently move water to ensure immediate access to hot water and effective heat distribution. They operate by using an impeller to create pressure dynamics that facilitate continuous water flow, allowing heated water to circulate between the boiler and radiators or other heat exchangers. Understanding their design and operation is crucial for optimizing heating system performance.
Car Battery – What's Inside?

This lesson provides an overview of the structure and function of a car battery, highlighting its main components, including the plastic case, lid, terminals, and internal cells. Each battery consists of six cells connected in series, generating a total voltage of approximately 12.6 volts, with lead plates and straps facilitating the chemical reactions necessary for current flow. The lesson also explains the roles of positive and negative plates, the use of envelope separators to prevent short circuits, and the importance of the electrolyte solution in the battery’s operation.
Steam Heating Systems Basics hvacr

This lesson provides an overview of steam heating systems, highlighting their common use in various settings and their unique method of heat distribution without pumps. It explains the science behind steam generation, the process of steam distribution and heat transfer, and emphasizes the importance of preventing issues like steam binding and steam hammer through the use of thermostatic radiator traps. Overall, the lesson underscores the efficiency and functionality of steam heating systems in maintaining warmth in buildings.
What is a diode?

In this lesson, we explored the fundamental concept of diodes, which are electronic components that allow current to flow in only one direction, functioning like one-way gates for electricity. We discussed the importance of correctly identifying the anode and cathode, the distinction between electron flow and conventional flow, and the applications of diodes in circuits, particularly in converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) through rectification. Additionally, we highlighted the role of capacitors in smoothing the DC output for stable voltage in electronic devices.
Half Wave Rectifier Explained – power electronics
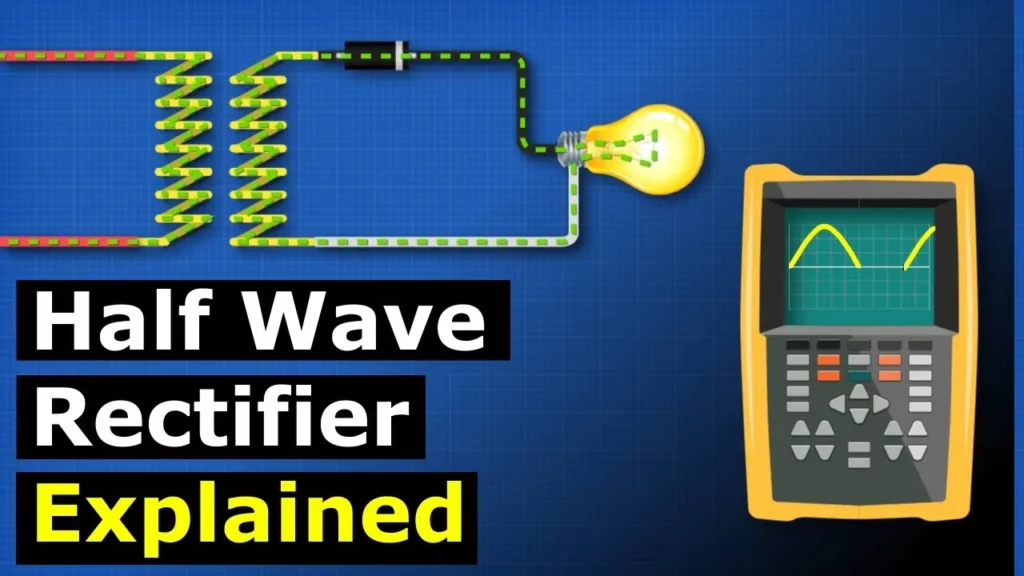
The lesson on half-wave rectifiers explains how these devices convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) using diodes, which allow current to flow in only one direction. It details the operation of a half-wave rectifier, where a diode blocks the negative half of an AC sine wave, resulting in a pulsating DC output, and discusses its applications in simple circuits, along with limitations such as flickering and inefficiency for sensitive electronics. To improve the output, the lesson suggests adding a capacitor to smooth the pulsating DC or considering a full-wave rectifier for a more stable power supply.