Thermal Comfort in Buildings Explained – HVACR Design
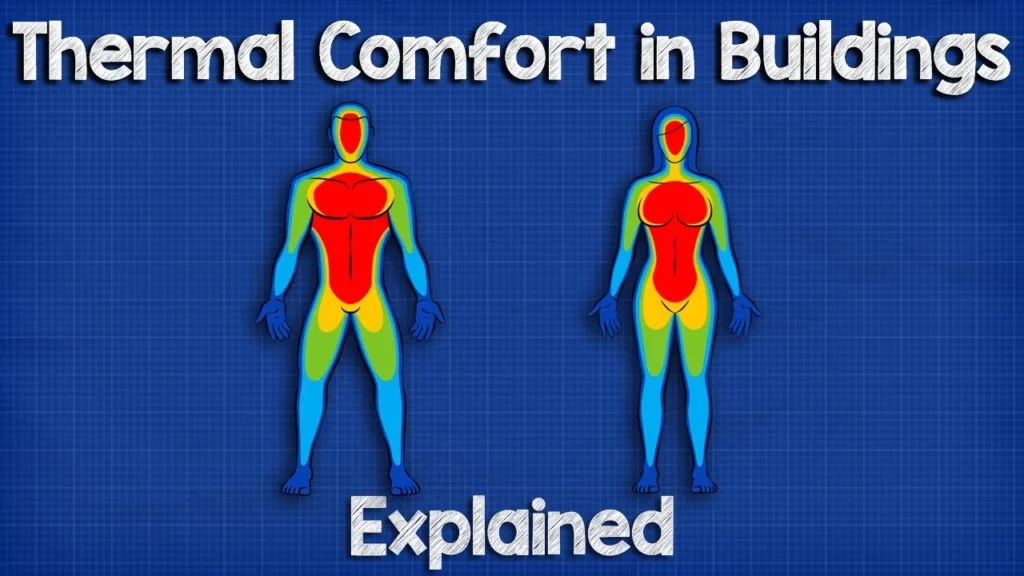
The lesson on thermal comfort in buildings emphasizes the significance of creating a comfortable indoor environment through effective HVAC systems, which manage heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Key factors influencing thermal comfort include temperature, humidity, air velocity, radiant temperature, metabolic rate, and clothing, all of which must be carefully balanced to ensure occupant satisfaction. The Predicted Mean Vote (PMV) metric is introduced as a tool to assess and optimize comfort levels within a space.
How to calculate the circumference of a circle
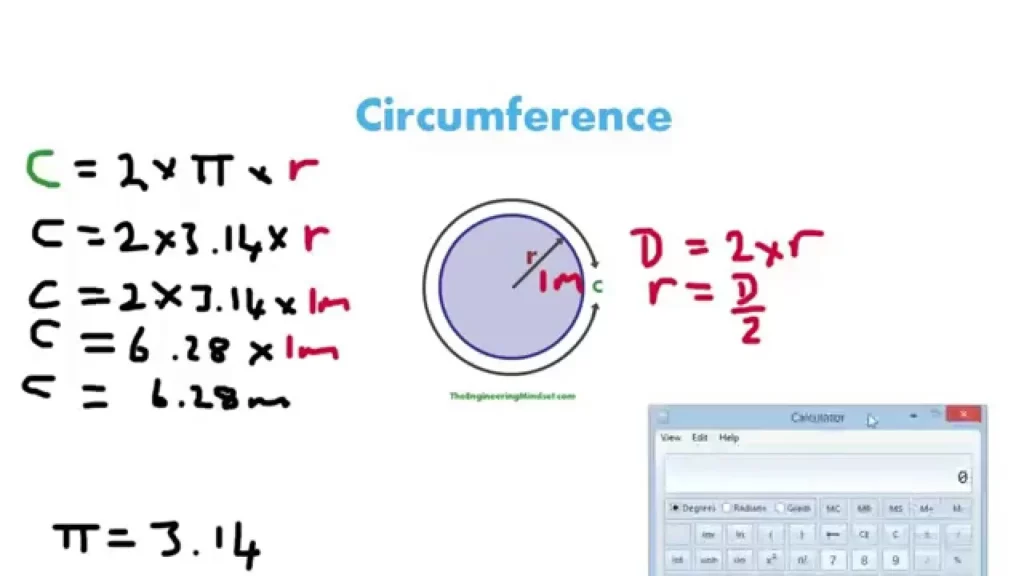
In this lesson, we learned how to calculate the circumference of a circle using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius. We also discussed how to find the radius from the diameter and emphasized the importance of double-checking calculations for accuracy. Additionally, we highlighted the fascinating fact that the ratio of the circumference to the diameter is always equal to pi (π), regardless of the circle’s size.
Centrifugal Pump How Does It Work
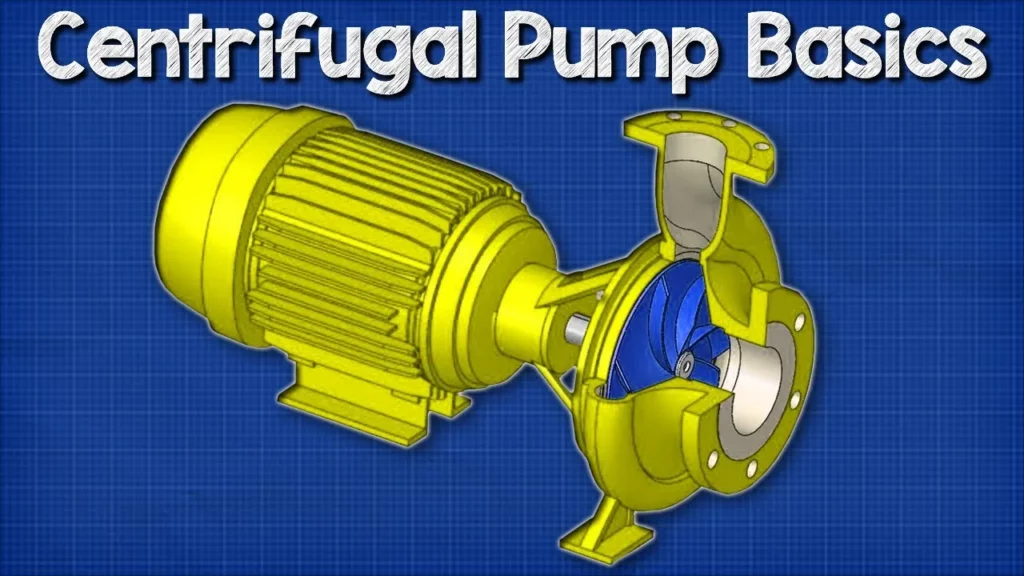
In this lesson, we explored the operation and components of centrifugal pumps, which are vital in various engineering applications, particularly in commercial and industrial settings. The lesson covered the pump’s structure, including the induction motor, impeller, and volute, explaining how these elements work together to efficiently circulate fluids by converting kinetic energy into static pressure. Additionally, we highlighted the reliability and longevity of centrifugal pumps, emphasizing their importance in maintaining systems across multiple industries.
Fundamentals of HVAC – Basics of HVAC
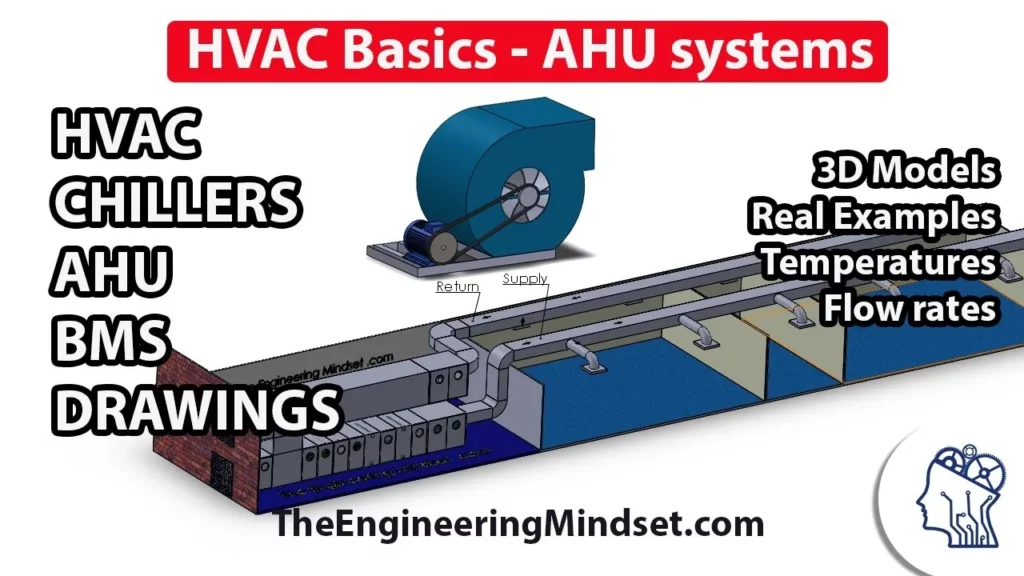
This lesson covers the fundamentals of HVAC systems, focusing on their essential role in maintaining comfortable and healthy indoor environments. It highlights the importance of the Air Handling Unit (AHU) in conditioning and distributing air, the significance of proper air filtration and temperature control through heating and cooling coils, and the role of fans in air movement. Additionally, it introduces the Building Management System (BMS) as a key component for monitoring and optimizing HVAC performance.
HVAC Primary & secondary circuits

This lesson provides an overview of the primary and secondary circuits in centralized HVAC systems, highlighting their roles in efficient temperature regulation within commercial buildings. The primary circuit generates temperature-controlled water using chillers or boilers, while the secondary circuit distributes this water throughout the building via various heat transfer equipment. Understanding the interaction between these circuits, along with the function of the common header, is crucial for optimizing HVAC performance and energy efficiency.
Micro Plate Heat Exchanger (MPHE) – How they work, working principle hvac phx

Micro Plate Heat Exchangers (MPHEs) represent a significant advancement in heat exchanger technology, offering enhanced efficiency in thermal energy transfer compared to traditional models. Utilizing a unique design with small dimples for improved fluid distribution and a counterflow configuration, MPHEs provide benefits such as reduced refrigerant volume, lower pressure loss, and up to 40% higher heat transfer rates. Their compact size and ease of installation make them ideal for modern heating and cooling systems, contributing to more sustainable energy solutions.
How Transformers Work: The Basics

This lesson explains the fundamental principles of how transformers operate, focusing on the relationship between electrical current and magnetic fields. It highlights the importance of alternating current (AC) in inducing voltage through coils, the role of a ferromagnetic core in enhancing efficiency, and the challenges of energy loss due to resistance and eddy currents. Ultimately, the lesson emphasizes that transformers can change voltage but not frequency, making them essential components in electrical engineering.
???? Chiller – Compressor Types

The lesson provides an overview of the four main types of refrigerant compressors used in chillers: centrifugal, screw, scroll, and reciprocating compressors. It explains the operational mechanisms of each type, their common applications, and highlights the shift towards more energy-efficient technologies as older models become less prevalent. Understanding these compressors is essential for effectively identifying and working with them in various real-world settings.
Engineering a Top Secret WW2 bunker industrial engineering ventilation hvac

This lesson explores the engineering and design of a World War II bunker in North London, highlighting its robust construction and essential building services that ensured its functionality and protection during the war. Key features include advanced ventilation systems that utilized heat recovery and air filtration to maintain air quality, as well as a reliable electrical system with backup power to support critical operations. The bunker serves as a historical testament to engineering ingenuity, although it now faces preservation challenges due to deterioration.
Transformers: How They Increase Voltage

This lesson explains the function and principles of transformers, which are devices that adjust voltage levels in electrical circuits. It highlights the difference between step-up and step-down transformers, emphasizing that while transformers can increase or decrease voltage, they do not create energy; they merely transfer it, maintaining a constant product of voltage and current known as apparent power. Additionally, the lesson discusses the concepts of power factor and reactive power, illustrating the importance of efficiency in connected devices to optimize energy usage.