10 Engineering projects Tackling Ocean Pollution #TeamSeas

The lesson highlights innovative engineering projects aimed at combating ocean pollution, spearheaded by organizations like TeamSeas.org, which seeks to remove 30 million pounds of trash from waterways. Various creative solutions are presented, including robots like Waste Shark and ClearBot, artificial coastlines, and technologies like the Bubble Barrier and Interceptor, all designed to efficiently collect and manage ocean waste. The lesson emphasizes the importance of collective action and encourages individuals to contribute to these initiatives.
How Chiller works – Design Data
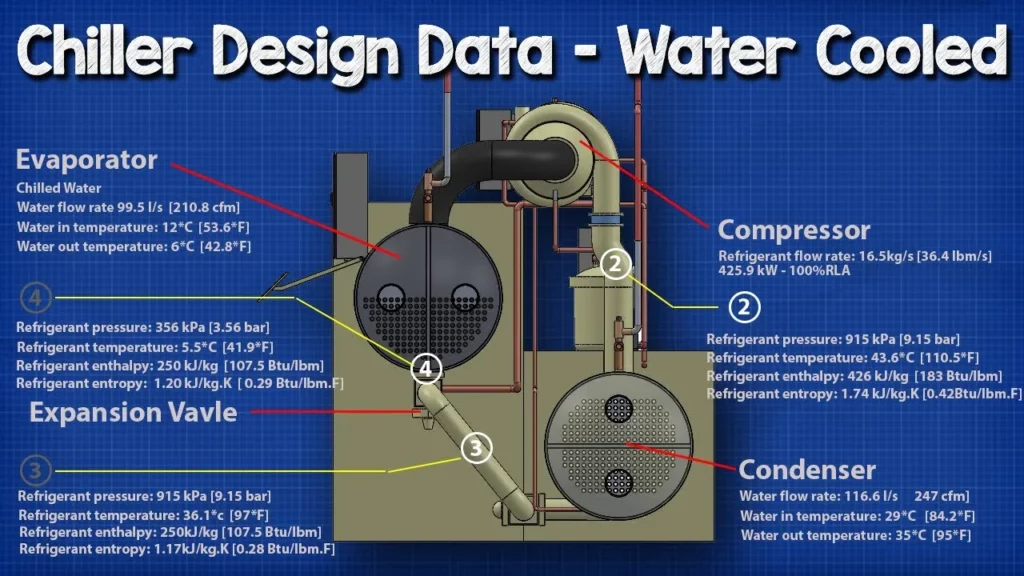
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of centrifugal chillers, focusing on their design, operation, and key components, including the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. It explains the thermodynamic cycle of a centrifugal chiller using a pressure-enthalpy chart, detailing the changes in pressure, temperature, and enthalpy throughout the refrigerant’s journey. Understanding these concepts is crucial for optimizing HVAC systems and assessing chiller efficiency and performance.
Fan & motor CALCULATIONS, Pulley size, RPM, air flow rate cfm hvac rtu
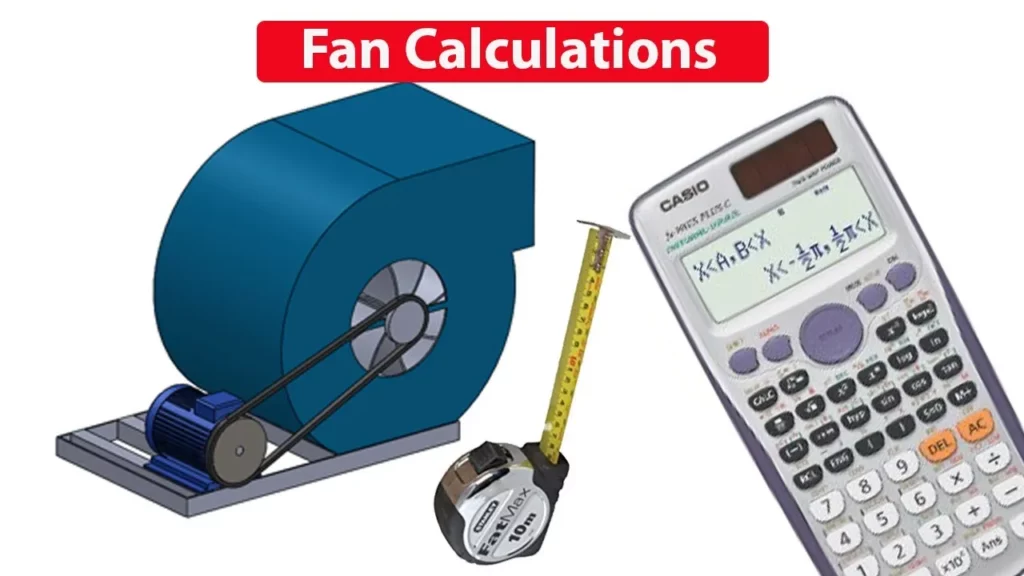
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of fan and motor calculations essential for HVAC systems, focusing on determining pulley sizes, RPM, and airflow rates. It outlines key formulas for calculating fan and motor pulley diameters, as well as how to adjust these parameters to optimize system performance and energy efficiency. By mastering these calculations, you can effectively design or modify HVAC systems to ensure they operate efficiently and meet specific airflow requirements.
Chiller – Cooling Capacity Control
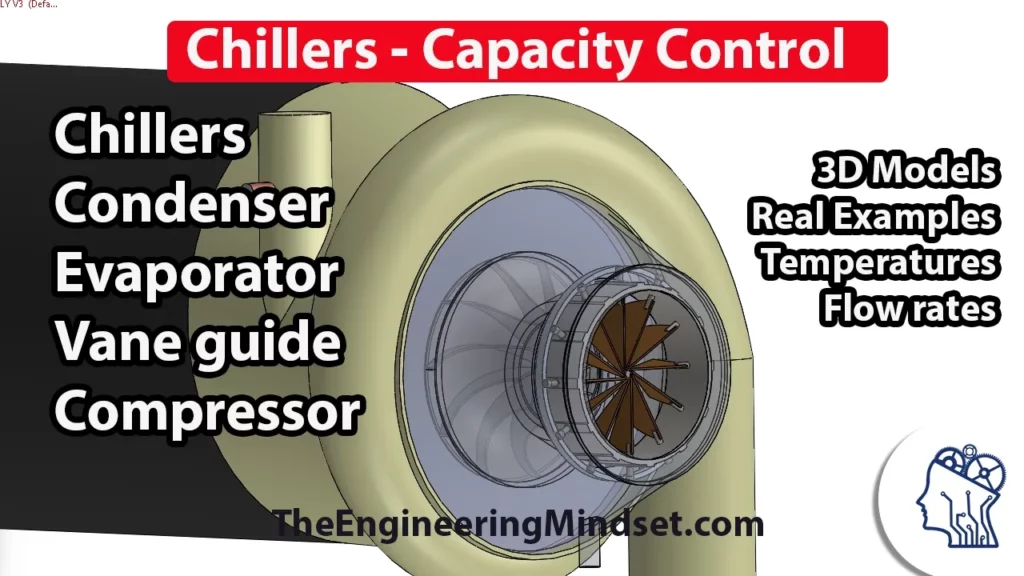
This lesson focuses on chiller capacity control, specifically examining the role of vane guides in centrifugal chillers. Vane guides are crucial for regulating refrigerant flow and maintaining the desired chilled water temperature, which is essential for efficient cooling operations in buildings. By adjusting the angle of the vanes, the system can optimize refrigerant flow and energy use, ensuring that the chiller operates effectively across varying capacities.
Why Are Solenoid Valves Used?
Solenoid valves are crucial for remotely and automatically controlling the flow of various fluids in systems, enhancing efficiency and safety without manual intervention. They are widely used in applications ranging from household appliances to industrial and HVAC systems, such as managing cooling in refrigeration and controlling fluid flow in manufacturing processes. Their versatility allows for precise control in critical operations, making them an essential component in modern engineering.
Pulley Belt CALCULATIONS – Belt length, distance between pulley wheels
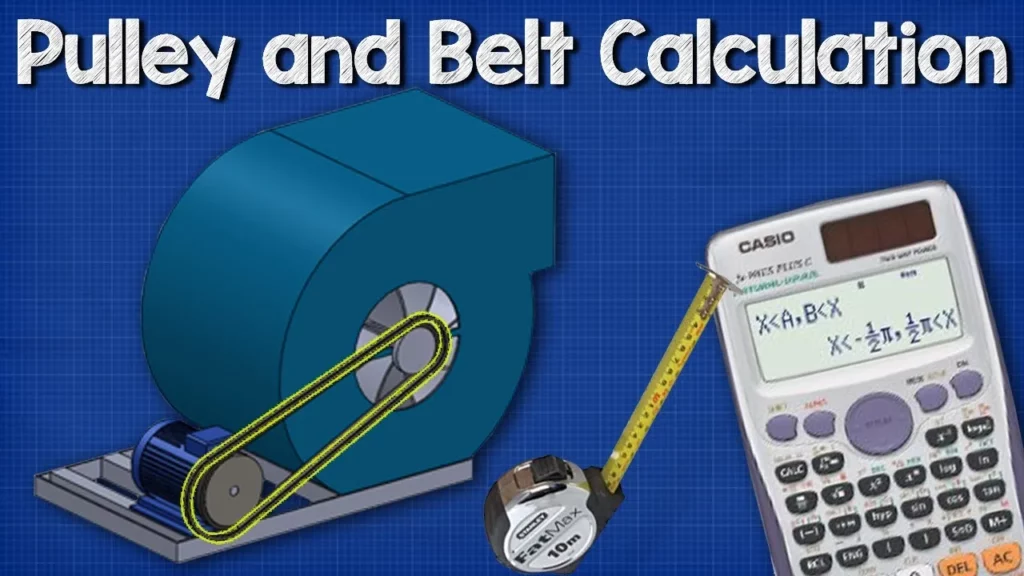
This lesson focuses on the essential calculations for determining belt length and the distance between pulleys in a pulley system, which is vital for various industrial applications like air handling units and conveyor belts. By understanding the sizes of the pulleys and the center-to-center distance, learners can accurately calculate the belt length and center distance, facilitating efficient design and maintenance of pulley systems. Utilizing tools like spreadsheet software can further streamline these calculations, enhancing both accuracy and efficiency.
Servo Motor, what's inside?

The lesson explores the inner workings of a servo motor, detailing its components such as the housing, gears, circuit board, and potentiometer. It explains how the motor converts high-speed, low-torque input into low-speed, high-torque output, and how it uses PWM signals to determine its position through feedback from the potentiometer. Overall, the lesson provides a comprehensive overview of how servo motors operate and are controlled.
Cooling Load Calculation – Cold Room hvac

This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of calculating the cooling load for a cold room, which is essential for maintaining the quality of perishable goods. It outlines the various sources of heat that must be accounted for, including transmission loads, product loads, internal loads, equipment loads, and air infiltration. By performing sample calculations and applying a safety factor, the lesson guides readers in determining the appropriate refrigeration unit size to effectively manage the cooling load.
Pump CALCULATIONS, Flow rate, RPM, Pressure, Power, Diameter

This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of essential pump calculations, including flow rate, RPM, head pressure, power, and impeller diameter. It offers formulas to help users determine how changes in RPM and impeller size affect pump performance, enabling better understanding and prediction of pump behavior for both existing and new installations. The guide emphasizes the importance of using accurate data and adjusting parameters to optimize pump efficiency.
How to DESIGN and ANALYSE a refrigeration system
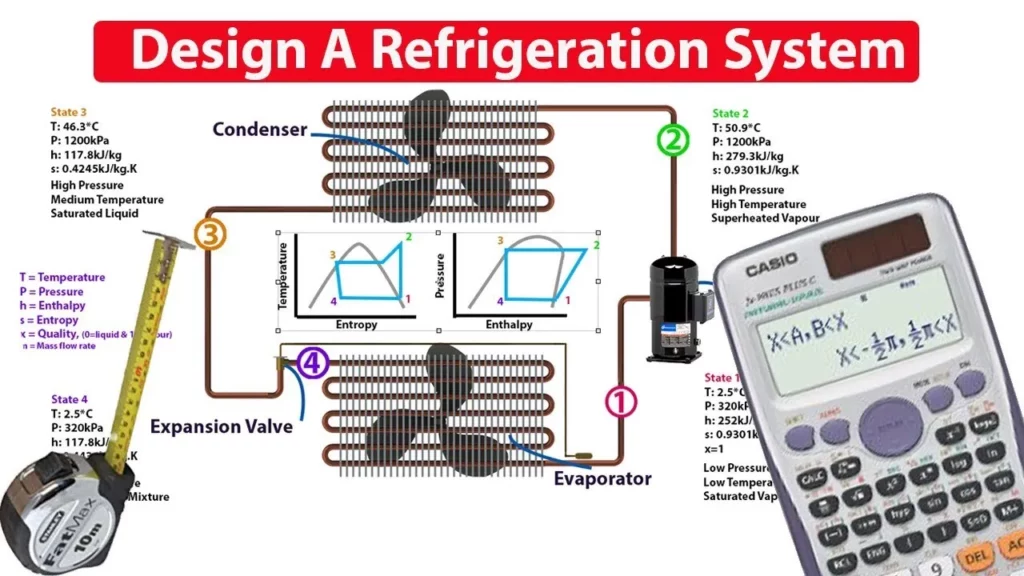
This lesson provides a comprehensive overview of designing and analyzing refrigeration systems, focusing on the ideal vapor compression cycle and its four main components: the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. It emphasizes the importance of understanding key thermodynamic properties at various points in the cycle, using refrigerant R134a as an example, and highlights how to calculate system performance through the coefficient of performance (COP). The lesson encourages starting with the desired cooling load to optimize system efficiency and performance.